Java 源码学习之java.util.LinkedList
LinkedList是Java编程中最常用的容器类之一,它是基于双向链接实现的,在面试时常常被与ArrayList作比较!
LinkedList容器在插入操作上效率很高,本文主要以他的构造函数,存储结构,增删改机制来介绍LinkedList
构造函数
先来看一下它的几个私有变量的定义:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
注释中描述的得清晰
size表示LinkedList列表的实际尺寸大小first和last分别表示双向链表的头部指针和尾部指针,默认都是指向nullNode为LinkedList中一个内部类,单个元素存储的实体,通过prev和next来建立双向链表
咱们在来看一下LinkedList的构造函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
LinkedList在它的构造函数上有一个无参构造器和集合类构造器,这个大致和ArrayList是类似的,少了一个指定初始容量构造器。
链表的添加
先来看下源码中链表添加元素的几个基础实现方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45/**
* Links e as first element.添加一个元素作为链表的头部
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;//如果链表里面还没有元素 则将第一个元素置为last 当然他同时也是first
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.//添加一个元素作为链表的尾部
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;//如果链表里面没有元素,则这个添加的元素为first,同时也是last
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.//在非空的succ之前插入元素
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
在上面的添加功能的基础实现方法中,linkFirst和linkLast这两个方法很容易理解,它们是通过改变头部指针或者尾部指针的指向来实现将元素直接添加到头部或者尾部,linkBefore这个方法这则需要指定一个插入元素的“坑”, 再往这个“坑”前进行元素添加,用图来表示: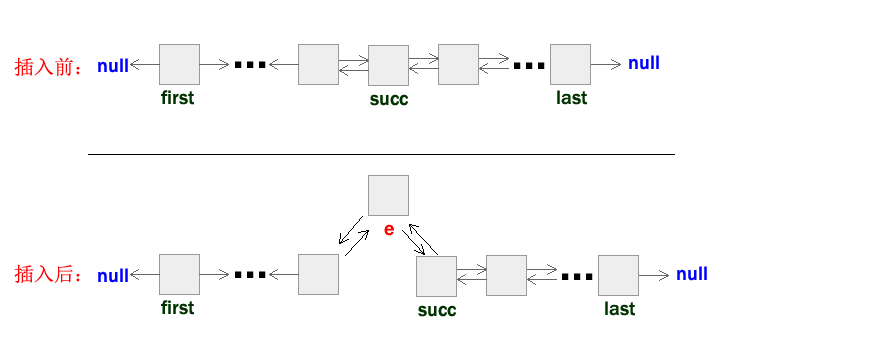
1 | /** |
上面源码中的方法均是LinkedList公开出来的方法,最终也都是调用了linkFirst,linkLast,linkBefore来完成操作的。
链表的删除
下面贴出来的是链表删除操作时的核心方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.//
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {//将fisrt指针指向f.next 也就是删除了f节点以及他之前的元素
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.//
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {//将last指针指针l.prev,也就是删除了f节点以及他之后的元素
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {//删除指定的元素x
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
删除方法中unlinkFirst和unlinkLast一眼看上去比较难理解,不过稍微盯几分钟画个图还是很好理解的
unlinkFirst(Node:将fisrt指针指向f.next 也就是删除了f节点以及他之前的元素f) unlinkLast(Node:将last指针指针l.prev,也就是删除了l节点以及他之后的元素l) unlink(Node:最容易理解,直接删除指定的x元素x)
1 | /** |
可以看到LinkedList删除里面的公开方法也都是直接调用了unlinkFirst,unlinkLast,remove
链表的get
LinkedList是基于链表实现的,其插入和删除元素方法都是在O(1)里面完成的,那么他的get方法又是如何做的呢?
1 | /** |
从源码的可以看到,LinkedList的get方法不能像ArrayList一样直接按索引取值,这里需要用遍历的方法来做,那当然在get上的复杂度肯定是要高于ArrayList了,不过LinkedList也做了一定的优化,从node(int index)可以看到,在按索引遍历的时候会根据索引所在位置(前半部分,后半部分)来决定遍历的方向:
- 当index<size/2的时候,从前往后取
- 当index>size/2的时候,从后往前取
Iterator方法
1 | private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { |
在ArrayList的iterator方法里面只提供了向后遍历,但是在LinkedList的iterator中可以发现他在提供hasNext的同时还提供了hasPrevious方法,所以这个iterator有双向遍历功能,既可以从前往后,也可以从后往前进行遍历,为我们在开发时提供了不少的便利
一些便利的方法
peek(),peekFirst()返回链表的头部但不删除,poll(),pollFirst()返回链表的头部同时将其删除peekLast()返回链表的尾部但是不删除,pollLast()返回链表的尾部同时将其删除offer(E e),offerLast(E e)在链表的尾部添加一个元素,offerFirst(E e)向链表的头部添加一个元素removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)移除第一次出现的元素,removeLastOccurrence(Object o)移除最后一次出现的元素
总结
LinkedList是基于双向链表实现的LinkedList的插入和删除的复杂度为O(1),(假设已有插入或者删除的元素),get的复杂度为O(N)LinkedList的迭代器有双向遍历功能
本作品采用[知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 2.5]中国大陆许可协议进行许可,我的博客欢迎复制共享,但在同时,希望保留我的署名权kubiCode,并且,不得用于商业用途。如您有任何疑问或者授权方面的协商,请给我留言。